Most cases include the skin. However, it is additionally common in other body parts with squamous cells. These are the respiratory and stomach-related frameworks and a few inner organs. It is the result of the over-the-top development of the cells that are not really from an epithelial covering. Its layering shows up as in case those of the developing or separating cells where it is inhabitant is the external layer of the skin, which is the cancerous layer that's something else alluded to as flaky patches, open sores, warty developments.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma is the foremost ordinary sort of skin cancer the world has experienced. Within the US alone, about one million modern cases are analyzed each year. The contrasts within the number of cases might moreover be related to distinctive climatic variations and hazard components; one of them is bright (UV) radiation, and the other is the wealthy hereditary inclinations there. Be that as it may, in spite of the increment in the rate of SCC as a plausible result of more sun presentation and the maturing of the populace, the circumstances in address were found to be on the rise.
SCC unquestionably does not evade the public. Yet, it is likely that more seasoned individuals get it to begin with. It is especially true for those who are over 50 years of age. The reason is that they are, for the most part, uncovered to the sun and the osmotic development of the malady afterward. Dark-skinned individuals may have the same tribulations as pale ones. However, a dark-skinned individual can be a casualty of this.

Squamous Cell Carcinoma is one of the most typical types of skin cancer. It also lies in the dermal layer of the skin. It makes it a risky place itself. Additionally, it is also a potential host of the lymph nodes as well as the rest of the body. For one, the tumor could already be in the body of the patient by the time of diagnosis, but in most cases, it's always in a very developed stage. It's at a stage that is very difficult to cure to the point of death.
Maybe, in the body, the position of the wounds is the most serious threat, above and beyond any of the other types of cancer. Ulcer is inclined to choose a specific place, like ears, lips, or genitals, which are the most defenseless parts of the body. For example, consider a case in which a scarred wound, a wound that heals for a long time, or an area exposed to X-radiation is more likely to relapse or develop if it occurs in a wound on a scar, a chronic one, or an area where radiation therapy was previously done.
The term squamous cell carcinomas is a name that was chosen due to some of the extruding features that they possess. They were given depending on their unique identifying marks. It has the most actual and visual cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) as the form that is observable on the skin. Still, at the same time, it can be seen in other internal organs like the lung space, the esophagus, and the cervix.
Keratoacanthomas meet the criteria for these specific squamous cell carcinomas, which some pathologists can pick up with their clinical skills. These kinds of malicious cells are the result of mighty proliferation. They are usually misdiagnosed as benign by most pathologists, yet they are malign, dangerous ones. A cancer that is like a wart and is not too invasive, verrucous carcinoma is a slowly progressing cancer in spite of the fact that it is very rough, which is actually quite counterintuitive. These cases are also very good types of evidence of the vast SCC spectrum. They depict extremely peculiar treatment needs.
If not treated promptly, Squamous Cell Carcinoma can lead to several complications. A major worry is the cancer's local invasion, where it begins to penetrate deeper skin layers and surroundings, causing both functional and cosmetic destruction. Infiltration of nearby nerves with SCC can lead to pain, numbness, or weakness.
Metastasis is the most critical complication. Despite being only present in the early stages, the latter can spread to lymph nodes, lungs, or other organs as the disease develops further, which complicates the treatment process. Results of the treatment- like scar formation or loss of function in the assigned area that needs surgical intervention- are not out of the question.
Protection from UV light for an extended period of time or the use of devices that emit UV light, such as solariums, for instance, is the main reason why squamous cell carcinoma, a type of skin cancer, occurs. Ultraviolet radiation, on the other hand, is a deciding factor disrupting the process of skin cells. For this reason, the genetic material in the skin cells is gradually altered, which leads to the development of cancer. This procedure is the main one. Increased exposure to ultraviolet radiation for a longer period of time is the main factor that can cause cancer cells to last longer.
An example of this is the intake of harmful substances such as arsenic and a few other chemicals, and, besides these, smoking. The most common in such cases are chronic, inflamed, and irritated conditions. Such problems are the result of burns and ulcers that do not heal. There are rare cases when the virus, for the most part, human papillomavirus (HPV), can be transmitted by one of the persons who have had it to the other members and then develop squamous cell carcinoma in the vaginal or oropharyngeal areas.
Squamous cell carcinoma basically occurs when there are persisting symptoms that do not recover. The ones who have them can get rid of them. A center depression, which is a general lesion attribute due to as-developed growth, is a common lesion feature.
The SCC type is described by putting a blemish or wounding the affected skin area through the treatment. The natural dark spots on the face, neck, and hands are the places where the sunlight is the strongest. Places like these may show early signs of skin cancer, like growths or small spots on the skin. The ulcer will transform into a chronic condition. Thus, it is the main cause of leukoplakia or urban and rural death of skin cancer, which affects the mucosa, i.e., the oral cavity and the throat. Besides the pain or itchiness, the reported site may also sustain inconvenience and hypersensitivity. Rapid identification of the disease is needed to launch the most relevant and timely treatment.
Diagnosis of Squamous Cell Carcinoma involves an initial physical examination of the lesion by a medical specialist. To do so, it is necessary to palpate the lesions cautiously to check their size. The shape and texture of the tumor are also important.
The absolute identification of SCC by biopsy is based on the collection of a biopsy sample and subsequent histopathologic analysis. Relying on the location and the size of the lesion, a medical professional may prepare a plan that includes other types of biopsies. Shave biopsy, which is just scraping off the epidermis, can be one of the ways to take a sample of a lesion. A punch biopsy is another incisional biopsy technique that usually gets a bit deeper sample from your skin. The doctor may also opt for an excisional biopsy that consists of the excision of the whole lesion.
Before scanning with CT, MRI, or PET, the disease can show signs of metastasis or invasion in deeper tissues. These are the investigations that help doctors gain a clear insight into the extent of the disease. They suggest interventions in line with the disease's nature. In case the probability of lymph node metastasis cannot be completely ruled out, a lymph node evaluation may be included in the tests.
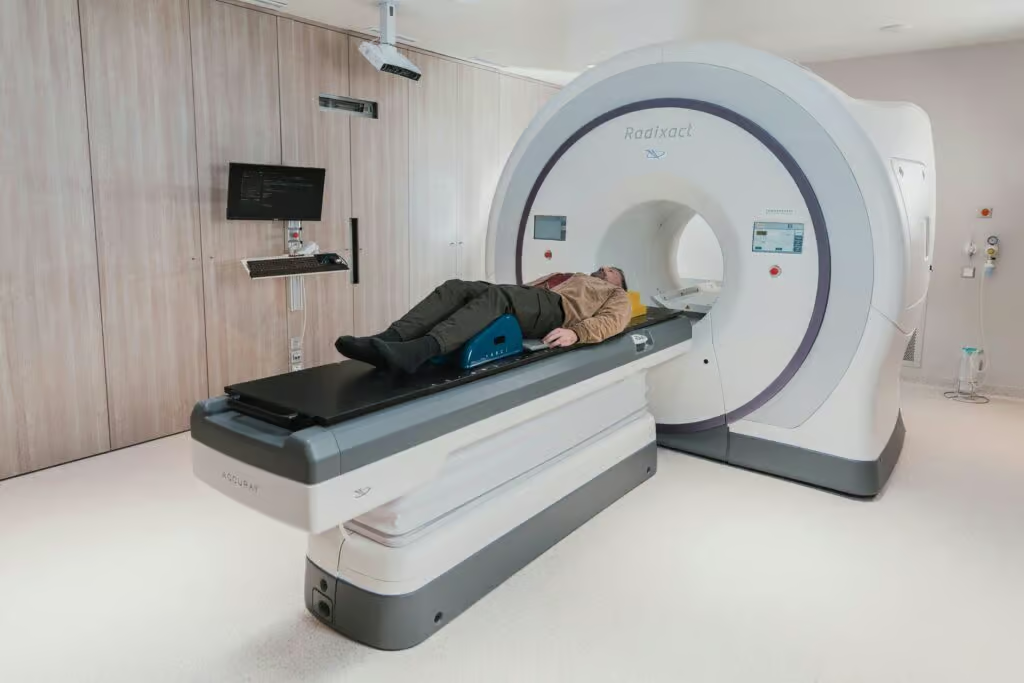
Management of Squamous Cell Carcinoma is based on patient profiles. Factors include tumor size, location, speed of growth, tumor state, whether it has spread, etc. The recommendation is to apply treatment to the primary or regional part of the tumor. It happens while the patient is still in the initial instance. Advanced cases necessitate further treatment, in addition.
Operating procedures are an important part of the treatment of skin cancer. Although people with low-risk features of SCC are usually treated with standard surgical practices, Mohs micrographic surgery is often required for those with a high-risk profile, such as the face. This process occurs in the sequence. A part of the tumor is removed using a micropulse laser system guided by the microscope. It is seen immediately on the monitor. The procedure continues until every single cancer cell is gone. Less tissue is removed, and the whole cancer area is removed invariably, and that is stressed.
Standard-wide excision is a form of excisional surgery in which doctors remove the tumor. This is done with a margin of normal skin around it to ensure the complete removal of cancer cells. For superficial SCC, curettage and electrodesiccation are used to scrape the tumor while the area is treated with heat or electricity.
When cancer tissue is inoperable or when a patient is unfit for surgery, radiation therapy is applied as a treatment for squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). In this carcass, the method is based on the emission of cyclotron ultrafast nuclear beams and their focus and delivery to cancer cells. Radiation is used as an additional therapeutic option for patients with difficult surgery.
Generalized therapies are adopted in the final stages of skin cancer with distant metastasis or squamous cell carcinoma. The success story of immunotherapy, which involves the use of the same miracle drugs as cemiplimab in cancer treatments, is a motivating factor. They can act immediately and effectively against the developed tumors.
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a non-invasive treatment modality that can be used in some cases of SCC. It is comprised of the application of a photosensitizer to the area of the irregular tissue. It is then exposed to a special source of light and is dying of proven fluorescence cancer cells. PDT is routinely used in cases of shallow cavities. Therefore, it is offered to patients who want to avoid scars or require RT.
At last, squamous cell carcinoma is an alarming health concern. However, with the possibility of early diagnosis and various treatment options, the majority of patients can gather the situation. The increased diagnosis and actions such as sun exposure awareness and regular skin checks could improve the quality of life in most of the people suffering from this condition.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) cases are usually not regarded as a medical emergency. There are some exceptions that the patient should not overlook, and they should consult the doctor immediately. In case one gets a lesion that all of a sudden grows at high speed, continuously bleeds, or is so painful that it restricts you from being able to do daily tasks, the progression is most likely an aggressive one, and that is why immediate medical examination has to be carried out. Besides this, the appearance of the scars of SCC around the high-risk areas like the lips, ears, or eyes might also be an indicator that the cancer has infected or is growing and thus requires connection with a specialist on time.
Another emergency medical care case also shows different nervous system symptoms. For instance, face paralysis or loss of sensation, which probably means that the cancer has invaded the neighboring nerves. The symptoms of metastatic spread, e.g., unexplainable weight loss, continued coughing, or swollen lymph nodes, also require the provision of a quick and prompt medical service.
Some skin problems look like Squamous Cell Carcinoma, and therefore, it is essential to give them careful treatment. The idea that actinic keratosis, which is the most frequent malignancy precursor mimicking SCC, is primarily confused. It starts as minor raised squamous papules on the sun-exposed parts of the skin. They have a rough and prickly feeling and are the early manifestation of cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is a kind of skin cancer. In some cases, it might be misunderstood as SCC. However, in the majority of instances, it is usually a slow-growing cancer likely not ending with metastasis.
Dermatitis, an inflammation of the skin, and psoriasis are autoimmune conditions that are the origins of flares on the skin that look rough or red at the beginning, confusing the initial diagnosis. Additionally, mycosis and bacterial skin infections sometimes result in chronic ulcers. They may not heal over a longer period. Thus, their diagnosis will be way more complicated than other skin issues.
There are several medical procedures, lifestyle changes, and psychological support that patients who have Squamous Cell Carcinoma are called upon to embrace to recover from the illness. The most common ways to keep an eye on the patient and to suspect that melanoma is returning are the regular checks patients have with a dermatologist or an oncologist. The medical specialist is the one who gives the advice most of the time, and he may use the following question to the patients: “You should consider whether using sunscreens with at least the SPF of 30, wearing the right clothes, avoiding activities that take place when there is too much sunshine is the right thing to do” are the options for them.
Simultaneously, skin problems are connected with the psychological functions of the disease, too. This is especially the invisible lesions that can cause problems with self-esteem and other mental health issues. There are some treatments that psychotherapists can apply that could be considered as the following: trying to rise above one's feelings or perceptions by maintaining a good understanding of one's illness and sharing it with the rest of the support group.
The stage of the tumor and the location(s) of it at the time of the diagnosis are the major factors for the prognosis of the patients who have squamous cell carcinoma. The disease cutaneous carcinoma (SCC) is the kind of cancer that is expected to be most easily cured. It has the highest cure rate of over 95% after therapy. Generally, cutaneous cancer is found on the skin's surface layer. But already at this point, the advanced stage of Squamous Cell carcinoma (SC) is quite dangerous, and the therapy method needs to be more aggressive, especially when cancer has spread to the lymph nodes or faraway organs.
In addition, the patient's condition of health, deficiencies of the immune system, and the existence of characteristics that raise the risks, such as the creation of tumors that are of poor quality, among others, are some of the other causes that may make the results go either way. The success of the research that came side by side with a good handle of immunotherapy and precision medicine greatly contributed to the longer period during which many patients survived.
Primarily, it is crucial to stay away from the variables that are known to be associated with squamous cell carcinoma. It is done in order to dodge the disease. Protection from UV rays by using sunscreen can be your best bet. Moreover, it is conceivable for people to veil the full spectrum of tanning beds by staying in the shade while tanning. More so, they can shield themselves with a big hat. Sun-protective clothing are also capable of blocking out harmful rays. That way, your skin will become more immune to ultraviolet radiation. You will be able to protect yourself from damage.
Also, checking oneself and looking for changes in the skin's appearance can give an early warning of precancerous or other worrisome lesions showing up. This is because it is a form of self-examination. Self-examination of the skin for sudden alterations, e.g., may even be logical in the process. It is possible for vendors to insist that people with a background in skin cancer or those who have been exposed to the sun go to dermatologists regularly.
Table of Contents